Chlorine »
PDB 3mvu-3n4a »
3n0p »
Chlorine in PDB 3n0p: A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor
Protein crystallography data
The structure of A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor, PDB code: 3n0p
was solved by
M.V.Kulkarni,
M.C.Tettamanzi,
J.W.Murphy,
C.Keeler,
D.G.Myszka,
N.E.Chayen,
E.J.Lolis,
M.E.Hodsdon,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 29.67 / 2.10 |
| Space group | P 65 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 123.540, 123.540, 73.330, 90.00, 90.00, 120.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 18 / 22.4 |
Other elements in 3n0p:
The structure of A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor also contains other interesting chemical elements:
| Sodium | (Na) | 3 atoms |
Chlorine Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Chlorine atom in the A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor
(pdb code 3n0p). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Chlorine atom.
In total only one binding site of Chlorine was determined in the A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor, PDB code: 3n0p:
In total only one binding site of Chlorine was determined in the A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor, PDB code: 3n0p:
Chlorine binding site 1 out of 1 in 3n0p
Go back to
Chlorine binding site 1 out
of 1 in the A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor
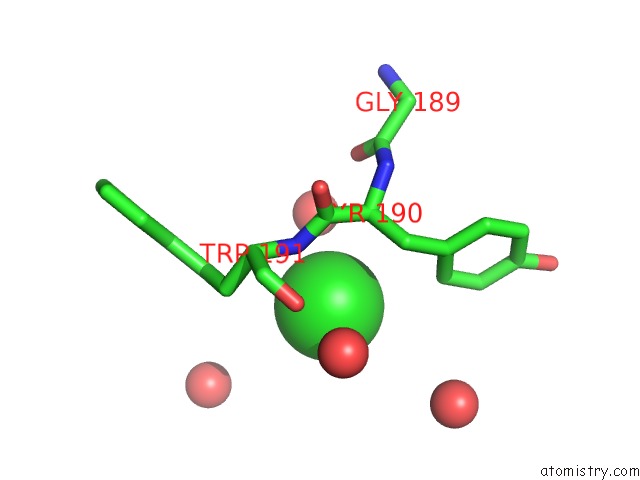
Mono view
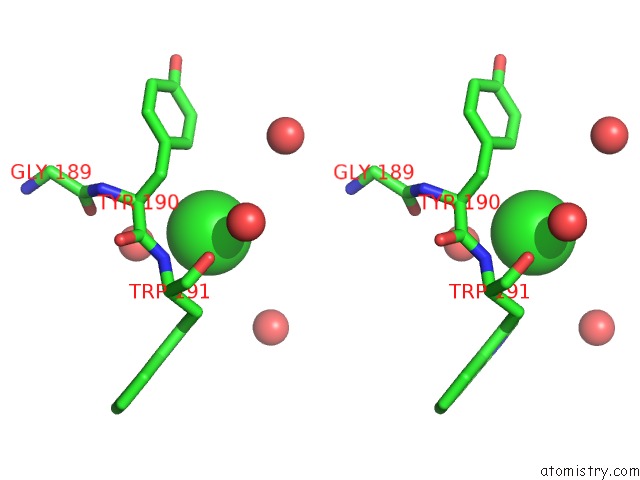
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Chlorine with other atoms in the Cl binding
site number 1 of A Mutant Human Prolactin Receptor Antagonist H30A in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Human Prolactin Receptor within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
M.V.Kulkarni,
M.C.Tettamanzi,
J.W.Murphy,
C.Keeler,
D.G.Myszka,
N.E.Chayen,
E.J.Lolis,
M.E.Hodsdon.
Two Independent Histidines, One in Human Prolactin and One in Its Receptor, Are Critical For pH-Dependent Receptor Recognition and Activation. J.Biol.Chem. V. 285 38524 2010.
ISSN: ISSN 0021-9258
PubMed: 20889499
DOI: 10.1074/JBC.M110.172072
Page generated: Sun Jul 21 00:31:11 2024
ISSN: ISSN 0021-9258
PubMed: 20889499
DOI: 10.1074/JBC.M110.172072
Last articles
Zn in 9J0NZn in 9J0O
Zn in 9J0P
Zn in 9FJX
Zn in 9EKB
Zn in 9C0F
Zn in 9CAH
Zn in 9CH0
Zn in 9CH3
Zn in 9CH1