Chlorine »
PDB 4cqc-4d0m »
4csw »
Chlorine in PDB 4csw: Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase, PDB code: 4csw
was solved by
M.A.Mcdonough,
R.Sekirnik,
C.J.Schofield,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 30.206 / 2.82 |
| Space group | C 1 2 1 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 158.300, 87.690, 90.610, 90.00, 113.10, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 16.83 / 20.96 |
Other elements in 4csw:
The structure of Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase also contains other interesting chemical elements:
| Manganese | (Mn) | 1 atom |
Chlorine Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Chlorine atom in the Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase
(pdb code 4csw). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Chlorine atom.
In total 2 binding sites of Chlorine where determined in the Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase, PDB code: 4csw:
Jump to Chlorine binding site number: 1; 2;
In total 2 binding sites of Chlorine where determined in the Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase, PDB code: 4csw:
Jump to Chlorine binding site number: 1; 2;
Chlorine binding site 1 out of 2 in 4csw
Go back to
Chlorine binding site 1 out
of 2 in the Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase
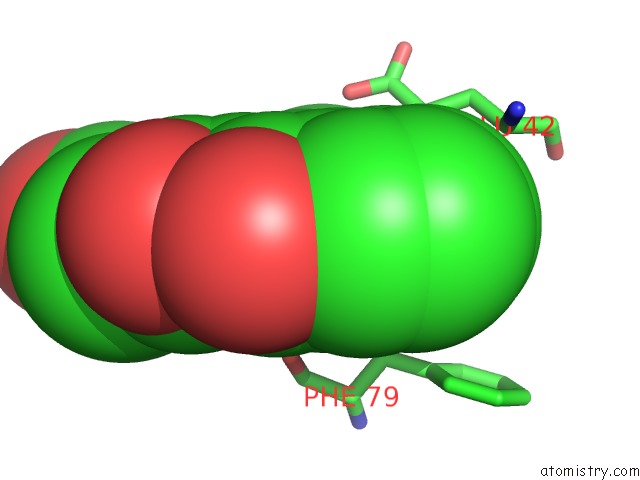
Mono view

Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Chlorine with other atoms in the Cl binding
site number 1 of Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase within 5.0Å range:
|
Chlorine binding site 2 out of 2 in 4csw
Go back to
Chlorine binding site 2 out
of 2 in the Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase

Mono view
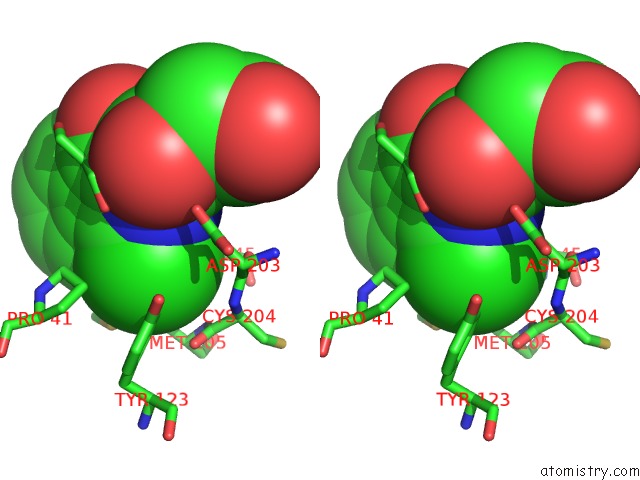
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Chlorine with other atoms in the Cl binding
site number 2 of Rhodothermus Marinus Ycfd-Like Ribosomal Protein L16 Arginyl Hydroxylase within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
R.Chowdhury,
R.Sekirnik,
N.C.Brissett,
T.Krojer,
C.-H.Ho,
S.S.Ng,
I.J.Clifton,
W.Ge,
N.J.Kershaw,
G.C.Fox,
J.R.C.Muniz,
M.Vollmar,
C.Phillips,
E.S.Pilka,
K.L.Kavanagh,
F.Von Deflt,
U.Oppermann,
M.A.Mcdonough,
A.J.Doherty,
C.J.Schofield.
Ribosomal Oxygenases Are Structurally Conserved From Prokaryotes to Humans. Nature V. 510 422 2014.
ISSN: ISSN 0028-0836
PubMed: 24814345
DOI: 10.1038/NATURE13263
Page generated: Fri Jul 11 14:07:20 2025
ISSN: ISSN 0028-0836
PubMed: 24814345
DOI: 10.1038/NATURE13263
Last articles
Fe in 2YXOFe in 2YRS
Fe in 2YXC
Fe in 2YNM
Fe in 2YVJ
Fe in 2YP1
Fe in 2YU2
Fe in 2YU1
Fe in 2YQB
Fe in 2YOO